Threaded-body cylinders (7)
Application
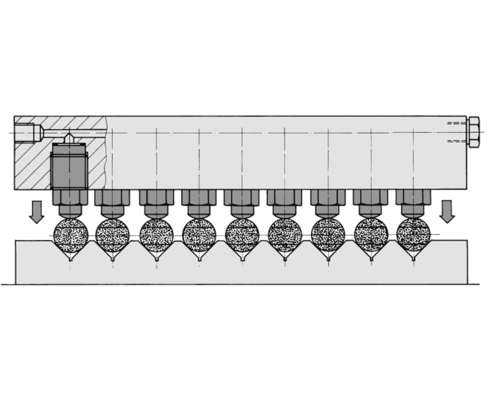
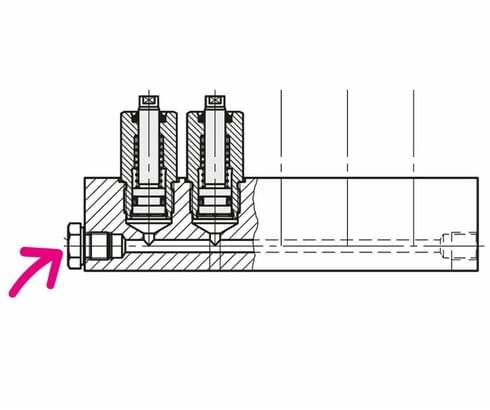
Threaded-body cylinders can be screwed directly into clamping bars or fixture bodies. Hydraulic oil is supplied through drilled channels. This enables very small cylinder distances in multiple clamping fixtures.
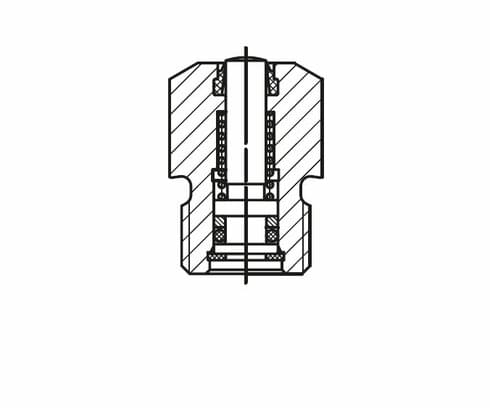
Single acting
As clamping cylinders, single-acting threadedbody cylinders with spring return are preferably used because only relatively short clamping strokes are required, and only one bore hole is needed for the hydraulic supply.
Venting of the spring area
A separate venting port is not provided for the short strokes of single-acting cylinders. If there is any danger that fluids penetrate into the spring area, only a series with wiper should be selected (see chart).
For threaded-body cylinders with plunger piston, the spring area is located on the hydraulic
side.
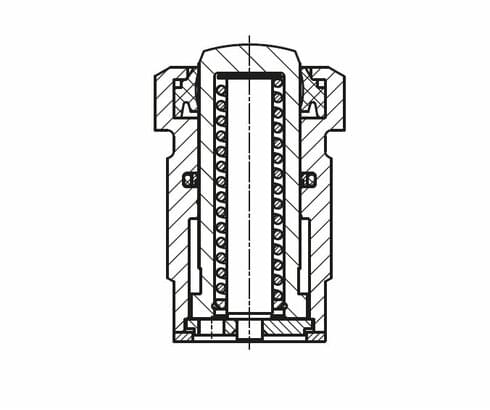
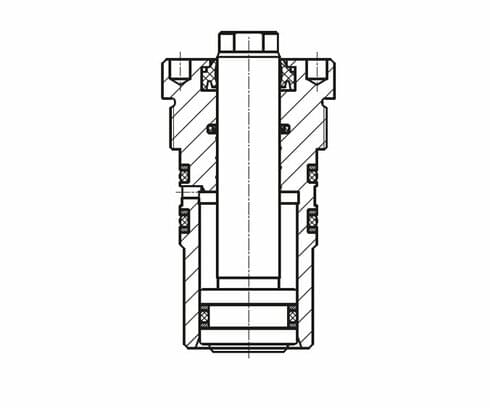
Double acting
Due to the longer piston strokes, these threaded-body cylinders can be used universally as
linear drives, i.e. pull cylinders. The return stroke is always effected within a certain period of time, which is particularly important for cycle-dependent installations.
Sealing type
The screwed-in cylinder bodies are sealed by cutting edge as for tube male stud couplings
- sealing ring flat seal made of POM
- cutting ring for direct pipe thread
- O-ring at the screwed plug
- O-ring / back-up ring with double-acting cylinders
Tightening torque
The required tightening torque is particularly important for the tightness and function of the
threaded-body cylinders. It depends on the screw-in thread and the sealing type.
The tightening torque can be taken from the respective data sheet or the operating manual.
Admissible piston side load
If the piston rod is loaded with a side load, higher wear must be expected. Threaded-body
cylinders are mostly used as clamping cylinders. Depending on the type, 3 to 5% of the push force at max. operating pressure is admissible in the clamping position.
The return stroke of single-acting cylinders must be free of side load, otherwise the force of the return spring is not sufficient.
Seals and max. operating temperature
The following elastomers are used as piston or piston rod sealing:
- NBR = Nitril-Butadiene-Rubber
Trade name e.g. Perbunan
Temperature range – 30 … + 80 °C - FKM = fluoro rubber
Trade name e.g. VITON®
Temperature range – 20 … + 150 °C
Further information, taking into account the common hydraulic fluids, can be found on data
sheet A 0.100.
Leakage
Threaded-body cylinders are leakage-free in static condition. When extending the piston
rod, the sealing lets pass only a micro-oil film to ensure the seal’s required lubrication and thus a high service life.
Bleeding
Air in the oil prolongs the clamping time considerably and leads to function troubles.
Therefore bleeding has to be effected during start up. As it is not possible to bled the threaded-body cylinders individually, screw plugs should be provided in the fixture body at the end of the drilled channels for bleeding.
Materials
Piston: case-hardening steel, hardened
Body: free-cutting steel, black-oxide
Mounting position
any, if not otherwise stated
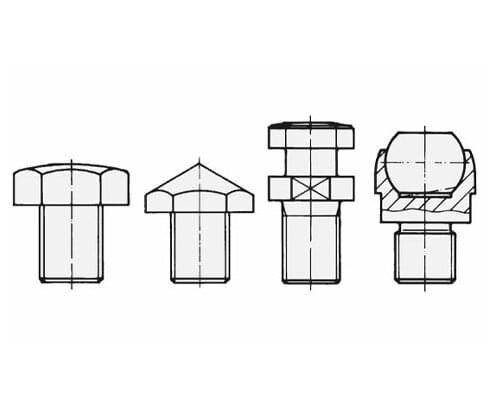
Accessory Contact bolts and coupling pins
Different contact bolts and coupling pins see data sheet G 3.800.
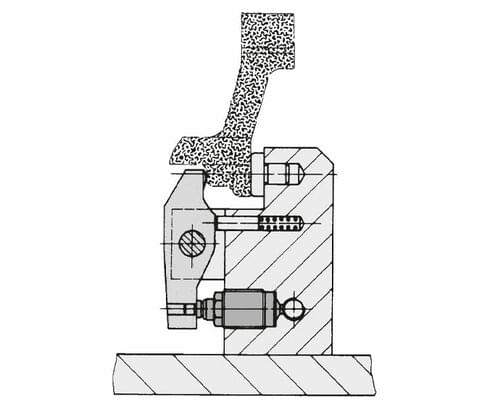
Application example
Take advantage of the free benefits of our login area:
- CAD data download
- Download operating instructions
Welcome back! Log in to your already existing user account.